What to Do When You Have Blue Balls
Last Updated December 20th, 2021
What are blue balls?
Blue balls are medically called epididymal hypertension (EH). Blue balls refer to testicular pain that occurs when the blood in the genitals is retained after prolonged arousal and is not dissipated by an orgasm. The condition is generally associated with men who are experiencing delayed ejaculation or reluctant ejaculation. The main reason for this phenomenon is the long sexual stimulation or arousal condition in which the penis stays erect, but without orgasm or ejaculation to occur.
During arousal, the sympathetic nervous system is off and there is an increased amount of blood that reaches the scrotum, testicles, and prostate region. During this process, the muscles in that region shrink. The purpose of this elevated amount of blood in this area is to maintain an erection during intercourse. When there is no ejaculation, the blood becomes more oxygen-poor but does not leave the area and in some cases produces a bluish appearing scrotum and hence the slang of Blue Balls is applied to this condition. During the process of vasoconstriction (the constriction of blood vessels, which increases blood pressure), testicles increase their size by 25 percent to 50 percent.
 The fastest way to get rid of pain caused by epididymal hypertension is through sexual intercourse. The process of ejaculation switches on the sympathetic nervous system which helps dissolve the blood in that area and gradually the symptoms disappear over time. Another way to get relief is from cold water shower or applying cold water to the scrotum. Applying cold water can increase blood circulation in the body and relieving the pressure. A severe form of vasoconstriction is called priapism, which requires medical treatment. Women can also suffer from this phenomenon. Women's genitals too experience an increased amount of blood flow during arousal and intercourse which causes congestion. If the woman does not reach orgasm, she may feel pelvic pressure and sometimes even pain.
The fastest way to get rid of pain caused by epididymal hypertension is through sexual intercourse. The process of ejaculation switches on the sympathetic nervous system which helps dissolve the blood in that area and gradually the symptoms disappear over time. Another way to get relief is from cold water shower or applying cold water to the scrotum. Applying cold water can increase blood circulation in the body and relieving the pressure. A severe form of vasoconstriction is called priapism, which requires medical treatment. Women can also suffer from this phenomenon. Women's genitals too experience an increased amount of blood flow during arousal and intercourse which causes congestion. If the woman does not reach orgasm, she may feel pelvic pressure and sometimes even pain.
Symptoms of blue balls
Blue balls or epididymal hypertension (EH) affects the testicles and may exhibit the following symptoms:
- Pain
- Discomfort
- Heaviness
- Aching
- Bluish discoloration of the scrotum.
Causes of Blue balls or epididymal hypertension (EH)
The main cause of blue balls or epididymal hypertension is due to the vasoconstriction in the genitals. When a man becomes sexually aroused, the arteries that carry blood to the genitals swell, while the veins that leave the genital area become small, allowing less blood to escape. This infrequent blood flow increases the amount and pressure of blood flow and retains it in the genital area.
The pressure which is formed is responsible for producing an erection and makes the testes to swell and makes them 25 percent to 50 percent larger than their normal size. If a climax is attained, the blood vessels quickly will return to their normal size and the amount of pressure in the genitals release and they return to their normal level. In other cases when a man is aroused and does not have a climax, blood flow in the genitals collects through a process called vasocongestion and may create sensations of aching, heaviness, and discomfort.
 Due to the long time the blood is trapped in the genitals, the blood is oxygen deprived and the color of the scrotum turns to blue from the accumulation of deoxygenated blood in the testicles. Oxygen-rich blood on the surface of the skin creates a red color, while blood with little oxygen appears blue. The longer the blood stays in the testes and scrotum without circulating to the heart and lungs, the less oxygen it obtains and the bluer the skin appears. Epididymal hypertensionusually does not last long and often the pain associated with blue balls is minimal.
Due to the long time the blood is trapped in the genitals, the blood is oxygen deprived and the color of the scrotum turns to blue from the accumulation of deoxygenated blood in the testicles. Oxygen-rich blood on the surface of the skin creates a red color, while blood with little oxygen appears blue. The longer the blood stays in the testes and scrotum without circulating to the heart and lungs, the less oxygen it obtains and the bluer the skin appears. Epididymal hypertensionusually does not last long and often the pain associated with blue balls is minimal.
It is common for men to become frustrated when they get an erection during sexual activity, but do not achieve climax. Due to this failure to achieve climax can lead to psychological stress and physical discomfort for men.
Other causes of testicular pain
The pain and discomfort in the testicles only when a person is aroused is most likely a result of epididymal hypertension. Pain occurring in the testes when not aroused may indicate other problems. Testicular pain can be caused by other diseases that can be localized to the testes or elsewhere in the scrotum.
Other conditions causing testicular pain include:
- Infection with chlamydia: Chlamydia and gonorrhea infection can cause inflammation of the epididymis causing severe pain to the testicles.
- Epididymitis (inflammation of the testicles): It is an inflammation of the coiled tube, which is present at the back of the testicle that carries and stores the sperm. Due to the inflammation, it causes severe pain to the testes.
- Hydrocele (swelling of the scrotum): Hydrocele is a type of swelling in the scrotum that occurs when fluid collects in the thin sheath surrounding the testicle. A hydrocele is common in newborns and usually disappears without treatment. A hydrocele is known to cause pain in the testes.
- An inguinal hernia: An inguinal hernia is defined as a lump or bulge in the inguinal area. These inguinal hernias develop when fatty or intestinal tissues protrude through a weakened abdominal wall.
- Kidney stones: Kidney stones are deposition of minerals that form on the inner lining of the kidneys. These kidney stones do not cause any problems until they remain in the kidney but can cause serious problems including severe pain when they move out of the kidney to the bladder.
- Mumps: Mumps or orchitis caused by a bacterial infection most commonly develops from the course of epididymitis, which is an infection of the tube that carries semen out of the testicles. This condition is called as epididymal-orchitis.
- Retractile testicle: Retractile testicle is a medical condition when a testicle retracts into the abdomen, which occurs in boys. This condition can cause severe discomfort and pain.
- Scrotal tumors: Tumor, cysts, spermatocele, epididymitis, and torsion of the epididymal appendix all affect the epididymis and may present as a mass or nodule and are known to cause testicle pain.
- Spermatocele: A spermatocele is a fluid-filled sac that grows in the epididymis, which is a small tube near the upper testicle that collects and transports sperm. Spermatoceles vary in size and could cause pain if they grow too large.
- Testicular trauma: Testicular trauma occurs due to an injury to the testicle. The injury caused to the testicle or scrotum can alter the configuration of these organs. When the testicle's tough cover is torn or shattered, blood leaks from the wound and stretches the scrotum until it is tense, and can lead to infection
- Testicular torsion (twisted testicle): Testicular torsion occurs when atesticle rotates and this, in turn, twists the spermatic cord and alters the blood to the scrotum. The reduced amount of blood flow may induce severe pain and swelling.
- Testicular cancer: Testicular cancer is defined as the lump on the testicles. Symptoms of testicular cancer include swelling, pain, and/or lumps in the testicles or groin.
- Varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum): A varicocele is an enlargement of the veins within the loose bag of skin that holds the testicles.
Treatment for blue balls or epididymal hypertension
 Ignore the problem: The pain of blue balls is not considered to be harmful and carries no side effects. There is virtually no medical treatment required for treating blue balls and generally subsides when the problem is ignored.
Ignore the problem: The pain of blue balls is not considered to be harmful and carries no side effects. There is virtually no medical treatment required for treating blue balls and generally subsides when the problem is ignored.
Do some heavy lifting: Doing some hard manual labor will help to blow off some steam and it actually works. Lifting heavy objects as well as pushing them induces a maneuver called Valsalva maneuver, which flexes the internal muscles as during a bowel movement. This, in turn, can release the pressure on the testicles and relieve the pain.
Work out: Anything that helps divert blood flow should help relieve the pressure off the swollen testicles. Jogging on the treadmill or doing a few push-ups can help the blood to move to other parts of the body and away from the scrotum.
Natural remedies: When the male sexual organ is aroused, there is a greater flow of blood to the penis following an expansion of the blood vessels. This leads to an erection. Sometimes the person does not orgasm for a long time. Epididymal hypertension is caused when a man does not orgasm for a while and instead has an extended erection. It can lead to a bluish hue on the testicles, which also become heavier; hence, the name blue balls for this condition. The presence of too much blood in the area of the genitals can cause pain and discomfort. This could be solved by taking garlic for two reasons: it can help to lower blood pressure and secondly, it is a natural aphrodisiac.
Refresh the mood: Changing the mood by concentrating on other aspects and reducing arousal is an easy way to divert the blood flow away from the genitals and provide relief to blue balls. Ignoring the thoughts which can lead to arousals such as thinking of a family member, taxes, or trouble at work should help in reducing the thoughts of arousal and this, in turn, relaxes the scrotum and releases the pressure off it.
Put an ice pack: An ice pack is a quick way to cool things down. The cold reduces swelling and therefore pressure and pain in the scrotum. It acts a shock to the system, which can help the person get off the arousal.
Get a cold shower: Taking a cold shower again seems to be beneficial. Taking a cold shower increases the blood circulation in the body. It also helps the blood which is trapped in the scrotum to release, reducing the pressure on the scrotum.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/health/mens-health/blue-balls#treatment
- http://www.soc.ucsb.edu/sexinfo/article/epididymal-hypertension-blue-balls
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11015532
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/11659104_Blue_balls
Facts
- Medically called as epididymal hypertension
- May cause bluish discoloration to the testes.
Facts
- This condition is generally painful.
- It usually affects men between the age of 15 and 30.
Facts
- During this condition, the testes swell up to 25-50% bigger.
- Masturbating or icing the area provides relief.
Subscribe to free FactDr newsletters.
REVAMP YOUR
LIFE
HEALTH
WELLNESS

If you're enjoying our website, we promise you'll absolutely love our new posts. Be the first one to get a copy!
Get factually correct, actionable tips delivered straight to your inbox once a week.
We hate spam too. We will never share your email address with anyone. If you change your mind later, you can unsubscribe with just one click

By clicking Subscribe, I agree to the FactDr Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of FactDr subscriptions at any time.
Was this article helpful?
Yes No
Dos and Don'ts
Dos
- Immediate relief can be achieved with masturbation.
- A cold shower can relieve symptoms.
- Distract your mind into something nonsexual.
- Slow music can also help.
- Keep yourself busy with other activities.
Don'ts
- Hide it from your doctor, if it is persistent.
- Engage yourself with sexual desires more often.
- Make a habit of masturbating on a daily basis.
Related Conditions
Trending Topics
Ferritin Test Ferritin test is a blood test that provides vital information on the level of RBCs and iron in…

Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary function tests (PFT's) are non-invasive breathing tests employed for diagnosing and monitoring lung diseases such as bronchitis
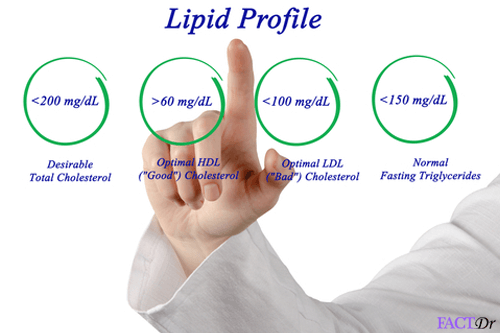
Lipid Profile Lipid profile is a blood test that provides complete information on how much cholesterol is present in the…
Rheumatoid Factor (RF) Rheumatoid factor or RF is a blood test used to diagnose painful joint conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis…
Rubella IgG Test The rubella IgG test is a blood test that checks for the rubella virus IgG antibodies present in…

DHEA Sulfate (DHEAS) Test DHEAS or DHEA Sulfate test is prescribed if an individual shows symptoms of abnormal adrenal actvity such as…

Thyroglobulin (TG) Test Thyroglobulin test helps in measuring and monitoring the concentration of thyroglobulin. This test can be used as a…

Urinary Microalbumin Test The urine microalbumin test is a urine test that measures the level of microalbumin or protein in the…


EKG – Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram, abbreviated as an ECG or an EKG, measures the electrical activity in the heart and used…

Post-Prandial Blood Sugar Postprandial blood sugar test is an important diabetes diagnosing tool. This simple blood test measure the level of…
Random Blood Sugar Test The random blood sugar or RBS test is prescribed mainly to check the level of sugar or glucose…

Erythropoietin (EPO) Test Erythropoietin stimulates the production of RBCs in bone marrow. An erythropoietin test is done to diagnose blood disorders…

HLA-B27 test The HLA-B27 is a blood test that is used to determine the level of a particular protein called…
Abdominal CT scan Abdominal CT scan is a diagnostic imaging technique that provides a clear picture of the state of internal…
![]()




Sputum test Sputum test is a commonly used diagnostic tool that is used to examine the presence of pathogens in…



Serum Zinc Test The serum zinc test is a blood test performed to assess the zinc level in the blood (serum)…

Beta 2 Glycoprotein 1 IgG Beta 2 glycoprotein 1 antibody test involves detecting and measuring the presence of the IgG class of beta…

Immunoglobulin M Test Immunoglobulin M is the largest and the first produced antibody which helps in the prevention or fighting of…



Serum Electrolyte If there is an electrolyte imbalance in the body, a serum electrolyte test will help to find out…
Anti Ds-DNA antibody Test The Anti Ds-DNA antibody test is used to diagnose the disease called lupus or more aptly the SLE(Systematic…

Dengue NS1 test Dengue NS1 is a blood test used to determine the onset of dengue fever. Dengue fever is transmitted…

Folate test The Folate test measures and monitors the levels of folic acid in the blood. This test is also…




Amylase Test Amylase test is done by checking the level of this protein in the blood sample and also in…

17 OH Progesterone test The 17 OH progesterone test is a simple blood test that is mainly used to diagnose the cause…
Bilirubin Test Bilirubin is a substance produced in the body as a result of red blood cell breakdown. A bilirubin…

LP-PLA2 Test The LP-PLA2 test is a test which is carried out to assess the levels of Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2…
Lipoprotein (A) Test Lipoprotein (A) test is used to measure and monitor the levels of LDL(Low-Density Lipoprotein) in the bloodstream in…

Vitamin B12 Test Vitamin b12 is an essential nutrient required for healthy functioning of the nervous system and also development of…

Beta hCG Test A Beta hCG test measures the level of human gonadotropin hormones present in the blood that is primarliy…

Tonometry Tonometry uses a device called tonometer to measure the pressure inside the eye. This pressure is depends upon…

Hepatitis Profile A hepatitis profile or a hepatitis panel is a blood test that checks for markers of hepatitis infection…


Blood Ketone (D3HB) Test The Blood Ketone Test measures and monitors the levels of ketone in the blood which is usually performed…


Beta 2 Glycoprotein 1 IgM The Beta 2 glycoprotein 1 IgM test detects IgM class of antibodies in the blood.The presence of beta-2…
Androstenedione Test Androstenedione is produced by the adrenal gland, the test of the levels of Androstenedione helps in the evaluation…



Copper Serum Test Copper serum test checks for abnormal levels of copper in the body. Both high and low levels of…

Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Arterial blood gas analysis is a diagnostic procedure used to determine the volume of oxygen and carbon dioxide…


Cardiac Profile Cardiac profile is panel of blood tests performed to check cholesterol level and other heart disease markers to…


Albumin Test Albumin test or blood serum test is a liver function test that measures the amount of the protein…
CA19.9 Test CA 19.9 is a cancer antigen that exists on the surface of cancer-causing cells. The levels of CA…




Hysteroscopy Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive tool to help specialists view the uterus to diagnose and even treat several…

Apolipoprotein -A1 (APO-A1) Test Apolipoprotein A-I (Apo-A1) constitutes 70% of protein content in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and helps in lipid metabolism.






Myelography Myelography is an important diagnostic tool that is used to investigate and identify abnormalities in the spine and…

Anemia Profile Anemia Profile test (Basic) is a blood screening test that measures the levels of important components of the…

Hymenoplasty Read on to find out all about hymenoplasty, the procedure, post-surgery care, the risks, and the benefits.





Thyroid Profile Thyroid profile is a panel of blood tests performed to check if an individual is suffering from any…






Cystoscopy Cystoscopy is intended to look at the abnormalities in the ureters, bladder, and urethra, to assist surgeries performed…
Cystatin C Test Cystatin C is a specific single-chain protein that is found in body fluids and is a biomarker for…




Thyroid Scan Thyroid scan is a diagnostic procedure that aims to view the thyroid gland and detect any growths or…
Rubella IgM Test The Rubella IgM test is a blood test that is performed to diagnose the presence of the rubella…

Malaria Antigen Test A malaria antigen test is a rapid diagnostic test (RDT) that can detect malarial antigens (proteins) in your…














Anti-Streptolysin-O Test The ASO or Anti-Streptolysin-O is a blood test designed to check for the presence of streptococcus bacterial infection…




Phimosis Read to know everything about phimosis, types, symptoms, treatment, risks and prognosis for patients with this condition.








Colposcopy Colposcopy is a simple, quick and non- invasive diagnostic tool to look closely inside the vulva, vagina, and…

Anoscopy Anoscopy is an invasive diagnostic procedure where a small device known as anoscope will be inserted in the…

Lipase Test A lipase test is a blood test performed to quantitatively measure the level of the enzyme lipase in…
Iron Deficiency Profile An iron deficiency profile is a battery of blood tests which are performed in order to determine the…

Ureteroscopy Ureteroscopy is the diagnostic procedure which is used for the detection of the kidney stones in addition to…





Electroencephalogram – EEG EEG or electroencephalogram is a diagnostic tool used to access the functioning of neurons and brain activity to…







Bone Marrow Biopsy Bone marrow biopsy is a diagnostic procedure where a small amount of bone marrow is extracted from hip…


Fructosamine Test A fructosamine test measures blood sugar glucose content. Fructosamine level can indicate blood sugar level in past 2-3…

Free PSA Test The free PSA test is used to detect the level or percentage of free PSA in the body…


Source: https://factdr.com/health-conditions/blue-balls/



0 Response to "What to Do When You Have Blue Balls"
Post a Comment